In recent years, metal printing has revolutionized manufacturing. A report by Deloitte stated that the additive manufacturing market is projected to reach $35.6 billion by 2026. This growth emphasizes the importance of understanding various metal printing techniques.
Metal printing is not just about producing parts; it's about innovation. As industries pursue efficiency, these techniques offer unique advantages. However, choosing the best method can be challenging. Each technique has its strengths and weaknesses.
Some methods are ideal for large-scale production while others excel in customization. Understanding these nuances is crucial for businesses. The right technique can lead to significant cost savings and improved performance. Yet, many companies struggle to keep up with evolving technologies.
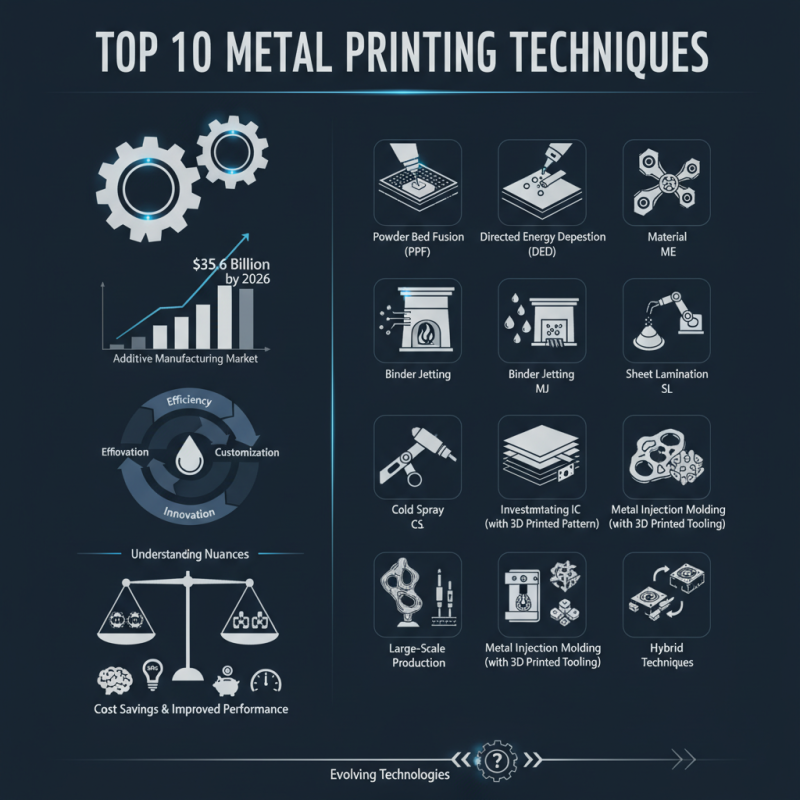
Metal printing techniques are crucial in various industries. Understanding these methods helps in choosing the right approach for specific applications. For instance, selective laser melting (SLM) is effective for creating complex geometries. It uses powerful lasers to melt metal powder layer by layer. This technique is popular in aerospace and medical fields.
Another method is electron beam melting (EBM). It works similarly to SLM but uses electron beams instead. EBM is particularly useful for titanium components. This technique is often chosen for parts that require high strength and light weight. Remember that each method has its challenges. Material properties can vary. Experimentation may be necessary to find the best fit.
Here are some tips: Always evaluate the component's design before selecting a technique. Incorporate feedback from specialists to avoid overlooking critical aspects. Lastly, consider post-processing needs. The chosen metal printing technique should facilitate further finishing work. Adjustments may be necessary as you refine your process. Embrace the learning curve; it's part of the journey.
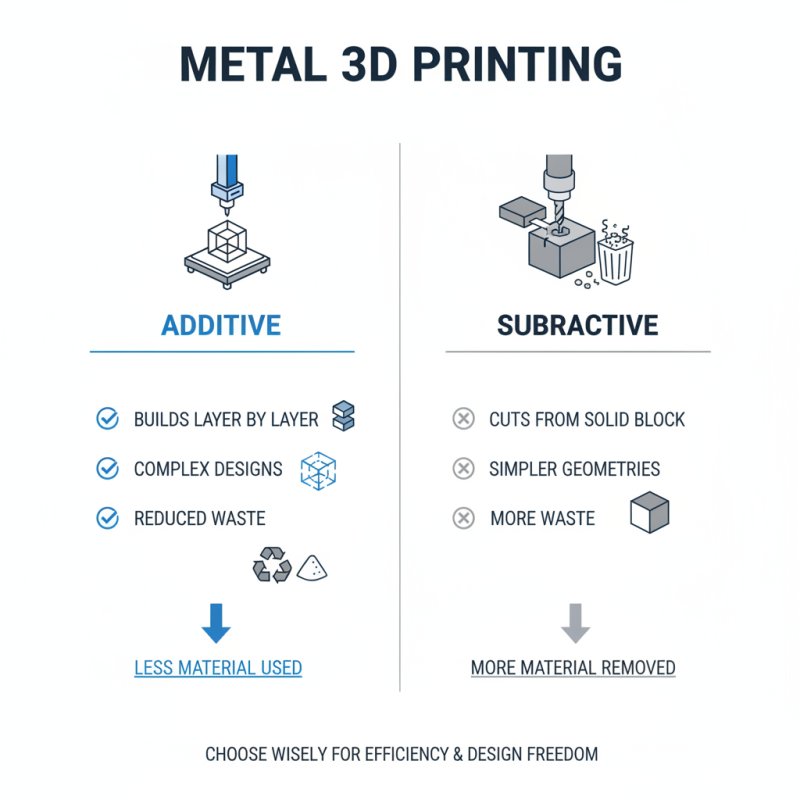
When considering metal printing, understanding additive and subtractive techniques is crucial. Additive printing builds objects layer by layer. It allows for complex designs that are hard to achieve otherwise. Materials are added only where needed. This method reduces waste significantly.
Subtractive printing, on the other hand, removes material from a solid block. It usually involves milling or grinding. This process can create strong, durable parts. However, it often results in greater material waste. Your choice deeply impacts the final product's quality.
Tips: Consider the project’s requirements before choosing a method. For intricate designs, additive might be best. For robust products, opt for subtractive techniques. Keep in mind that each method has its limitations. Always reflect on the desired outcome and rethink your approach.
When exploring these techniques, remember the cost implications. Additive methods can sometimes be more expensive per part. Subtractive processes might require more expensive machinery. Assessing your budget is as important as understanding the technology. Choosing the right technique can lead to innovations or, at times, unforeseen challenges.
When choosing metal printing materials, understanding their properties is key. Stainless steel is popular for its strength and durability. It resists corrosion and is ideal for outdoor applications. Aluminum, on the other hand, is lightweight and offers excellent thermal conductivity. It's perfect for parts that need to keep their weight down.
Titanium is a premium choice. It’s known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility. This makes titanium great for medical implants and aerospace parts. However, it can be challenging to work with. The machining process often requires special tools and techniques.
Tips: Always consider the specific application when selecting materials. Think about how the final product will be used. Also, don't overlook how post-processing will affect these materials. Some may require additional finishing, which can influence their overall properties. Regularly revisit and assess your choice of material; sometimes, the initial pick may not yield the best outcome based on later insights.
Metal 3D printing is a fascinating yet complex process. Understanding the steps is essential for success. It typically begins with designing a 3D model. Software is often used for this purpose. A skilled designer must consider the tolerances and specifications needed for the final product. This step can be challenging, especially for intricate designs.
Next, the fabrication of the metal part begins. The most common techniques include selective laser melting. This method uses a high-powered laser to fuse metal powder layer by layer. Each layer must be accurately aligned. Misalignment can lead to defects. After printing, the part requires post-processing. This may involve removing excess powder and surface finishing. These steps can be tedious but are crucial for achieving high quality.
Finally, the printed part is evaluated for structural integrity. This assessment can be subjective. Many factors influence the outcome, including material choice and print settings. Sometimes, failures occur, leading to further iterations. Learning from these mistakes is vital. Each project offers new insights that help refine the process. With practice, the art of metal 3D printing becomes clearer.
The landscape of metal printing technology is rapidly evolving. Innovations are pushing boundaries in this field. With each advancement, new possibilities arise for industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. These sectors increasingly rely on metal printing for complex parts that traditional methods cannot create.
One emerging trend is the use of artificial intelligence. AI can optimize printing processes, enhancing precision and reducing waste. It may sound impressive, but integrating AI into existing workflows poses challenges. There’s always the risk of over-dependence on technology. Additionally, achieving the right balance between human oversight and algorithmic efficiency is crucial.
Another focal point is sustainable practices. Metal printing can minimize material waste, but sustainability in production is still a work in progress. The demand for eco-friendly materials is growing. However, not all innovations prioritize environmental impact equally. The industry must continually reflect on its practices to ensure responsible growth. This balance between innovation and sustainability remains a significant hurdle.
The chart below shows the popularity and effectiveness of various metal printing techniques based on recent industry trends.






© Copyrights Levil Technology Corp 2022