The advent of the CNC 3D printer has revolutionized the landscape of manufacturing and prototyping, merging precision machining with additive layer technology. According to a recent report by Market Research Future, the global CNC machine market is expected to reach approximately $100 billion by 2025, largely driven by applications in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. With the ability to produce complex geometries and reduce material waste, CNC 3D printers are rapidly becoming an essential tool in modern manufacturing processes.
Industry expert Dr. Jane Smith, a recognized authority in additive manufacturing technologies, notes, “The integration of CNC systems with 3D printing allows for unprecedented levels of detail and customization in production.” This statement underscores the fundamental shift that CNC 3D printers represent in the industry—offering not only efficiency but also the capability to tailor products to meet specific client requirements. As businesses increasingly turn to CNC 3D printing, understanding its operational principles and benefits will be crucial for leveraging this technology effectively in various sectors.
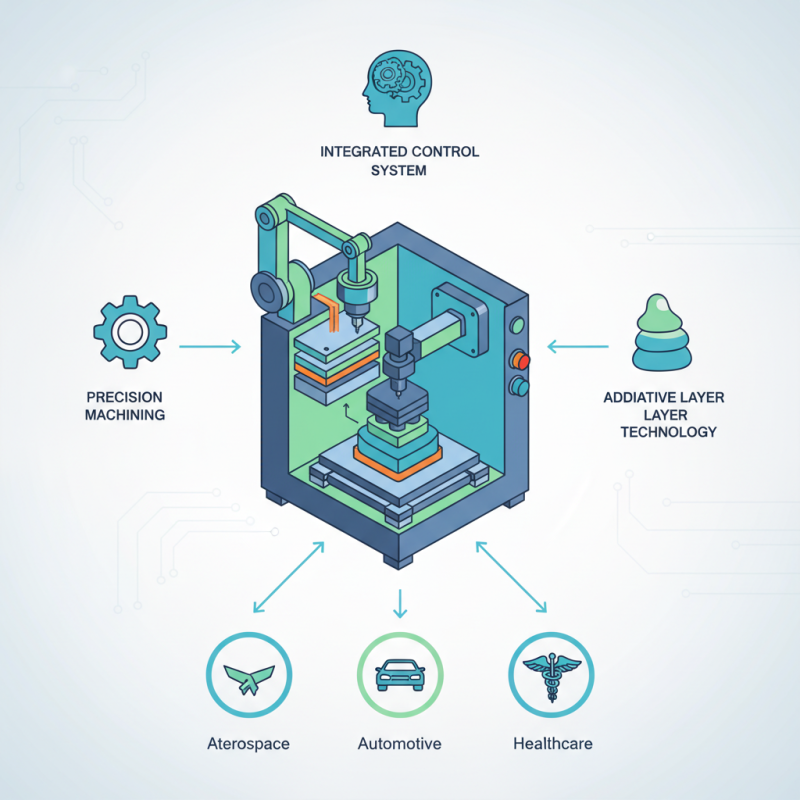
CNC 3D printers represent a significant advancement in additive manufacturing technology, merging traditional CNC (Computer Numerical Control) techniques with the capabilities of 3D printing. This innovative approach allows for the precise layering of materials, enabling the production of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional methods. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global 3D printing market is projected to reach $62.79 billion by 2028, highlighting the growing demand for efficient and versatile manufacturing solutions.
One of the key benefits of CNC 3D printers is their ability to work with a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and even ceramics. This versatility allows engineers and designers to easily transition between prototyping and production, eliminating the need for extensive retooling. Furthermore, the integration of computer-aided design (CAD) software streamlines the workflow, reducing lead times and minimizing errors in the manufacturing process.
**Tips:** When selecting a CNC 3D printer, consider factors such as build size, material compatibility, and resolution. Additionally, staying updated with software advancements can greatly enhance productivity and precision in your projects. For those entering the field, starting with a smaller-scale printer can provide valuable hands-on experience before advancing to larger, more complex systems.
A CNC 3D printer operates through a combination of advanced components that work together to create three-dimensional objects. The core components include the frame, which provides stability; the motion system, typically consisting of stepper motors and lead screws, responsible for the precise movement of the print head; and the print bed where the objects are built layer by layer. Another crucial part is the extruder, which melts the filament and deposits it onto the build surface, allowing for intricate designs to take shape.
Tips: When selecting a CNC 3D printer, consider the material compatibility of the extruder. Different filaments, such as PLA or ABS, require specific heated extruders to achieve optimal results. Additionally, a sturdy frame can significantly reduce vibrations, leading to improved print quality.
The electronic control board is another vital component that interprets the design files and coordinates the actions of the motors and extruder. Advanced boards may feature additional capabilities, such as auto-leveling, which ensures the print bed is perfectly aligned for consistent results. Proper maintenance of these components, particularly regular lubrication of moving parts, can enhance performance and longevity.
Tips: Regularly check and calibrate your CNC 3D printer to ensure that all components are functioning correctly. Simple adjustments can prevent many common printing issues, such as layer misalignment or poor adhesion.
| Component | Function | Material Used | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Print Head | Extrudes filament or resin to create layers | PLA, ABS, Resin | Prototyping, Hobbyist Projects |
| Build Platform | Supports the printed object during printing | Aluminum, Glass | Industrial Parts, Samples |
| Controller | Manages the movements of the print head and platform | Microcontroller Boards | Custom Designs, Engineering Projects |
| Stepper Motors | Control the movement on each axis | Electric Motors | 3D Printing, Automation |
| Cooling Fans | Cool down the material post-extrusion | Plastic, Metal | Various Printing Applications |
CNC 3D printing combines the precision of computer numerical control with additive manufacturing techniques, offering a sophisticated approach to creating complex structures. The process begins with designing a 3D model using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Once the design is finalized, it is sliced into thin horizontal layers, which the CNC printer will use to build the object layer by layer.
During the printing process, the CNC machine precisely controls the movement of the print head or nozzle, depositing material according to the specified design. The printer may utilize various materials—such as plastics, metals, or composites—depending on the desired characteristics of the final product. Each layer is meticulously laid down and allowed to solidify before the next one is added, ensuring a high level of detail and accuracy. Tip: Always double-check your slicing settings to avoid common issues like layer misalignment or material waste.
After printing, the object often requires post-processing, which can include sanding, painting, or assembling additional components. This final touch enhances the visual appeal and functionality of the piece. It's also a good practice to maintain your CNC printer regularly to ensure optimal performance. Tip: Keep your workspace clean and organized, as this not only boosts efficiency but also contributes to the longevity of your machinery.
This chart compares the number of units produced per month using different printing technologies, highlighting the prevalence of CNC 3D printing in the manufacturing sector.
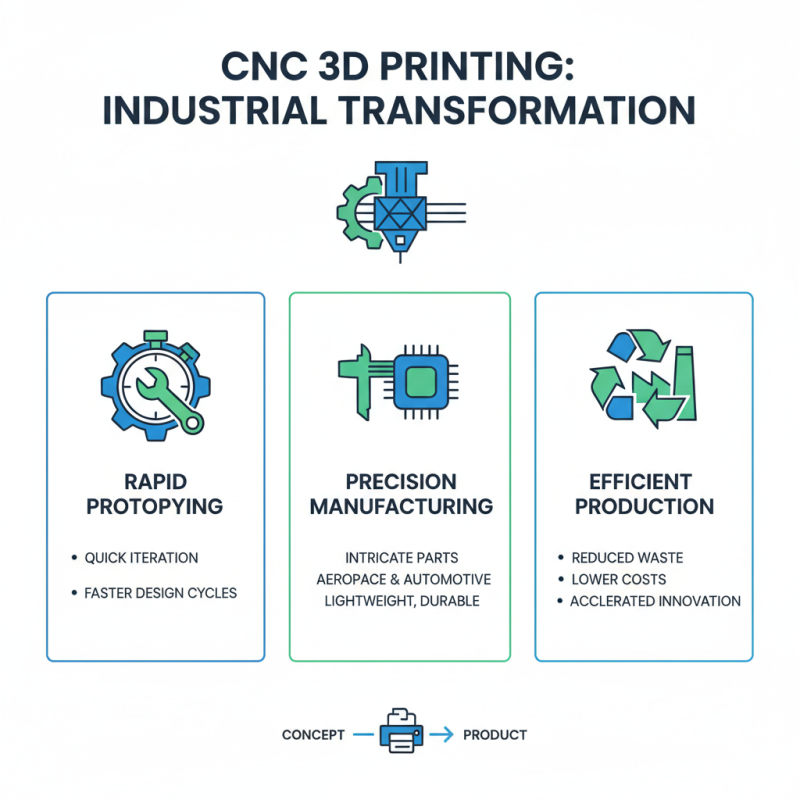
CNC 3D printing technology serves as a transformative tool across various industries, facilitating rapid prototyping and efficient production processes. In manufacturing, CNC 3D printers enable the creation of intricate parts with precision that traditional methods often cannot achieve. This capability is especially beneficial in sectors such as aerospace and automotive, where lightweight, durable components are essential. By leveraging this technology, companies can significantly reduce material waste and production time, leading to cost-effective solutions and enhanced innovation.
In the field of healthcare, CNC 3D printing is revolutionizing the way medical devices and implants are designed and produced. Tailored prosthetics and dental products, designed specifically for individual patients, improve comfort and functionality. Additionally, the ability to print complex organic structures opens new avenues in bioprinting, paving the way for advancements in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Similarly, in architecture and construction, CNC 3D printing allows architects to visualize and create complex forms, streamlining the design process and enabling the construction of customized structures efficiently. As this technology continues to evolve, its applications will likely expand, influencing numerous sectors with improved production methodologies.
CNC 3D printers represent a fusion of traditional manufacturing techniques and modern digital fabrication methods. One significant advantage of using CNC 3D printers is their ability to produce highly precise and intricate designs. The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software allows for a level of customization that is often unattainable with conventional manufacturing processes. This precision makes CNC 3D printers ideal for producing complex parts in fields such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare where exact specifications are crucial.
However, there are limitations to consider when employing CNC 3D printers. The initial setup and equipment costs can be substantial, particularly for high-end machines capable of working with various materials. Additionally, the speed of production can be slower compared to traditional methods, particularly for larger projects. Material limitations also exist; not all materials are suitable for 3D printing, and the choice of materials can affect the durability and functionality of the finished product. While CNC 3D printing offers remarkable benefits, it is essential to weigh these against the potential drawbacks when determining its suitability for specific applications.







© Copyrights Levil Technology Corp 2022